Xyleborus pubescens Zimmermann 1868
 Images: Displaying 1 to 8 of 12
Images: Displaying 1 to 8 of 12 
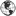
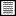
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
 Xyleborus pubescens (female)
Xyleborus pubescens (female) |
| Next > |

Xyleborus pubescens (female) lectotype Xyleborus pubescens Zimmermann. MCZ type No. 986. MCZ This image is the property of The Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University. Used with permission.
 Summary of Information
Summary of Information

SYNONYMY
Taxonomic Comments. This species is very similar to specimens from eastern North America identified as X. intrusus Blandford, differing in minute differences in the denticles of the elytral declivity. Xyleborus intrusus is found from British Columbia to Gautemala, but is isolated from eastern populations of the 'same species' by a large area in central Canada and the Lake states of the U.S. Bright (2019:298) formally proposed the synonymy but this may be premature. In the meantime I believe that all records and names from eastern North America should be treated as pubescens. Pérez Silva et al. (2021) cited X. pubescens from the Mexican state of Chiapas, further complicating matters. This group of species needs revision.
- Xyleborus pini Eichhoff 1868. Berl. Ent. Ztschr. 11: 401
- Xyleborus pubescens Zimmermann 1868. Trans. Amer. Ent. Soc. 2: 145
- Xyleborus propinquus Eichhoff 1869. Berl. Ent. Ztschr. 12 (3-4): 281
DISTRIBUTION.
Numbers in parentheses after each geographic unit are the number of distinct collection events in the database for that unit. For exotic species generally only countries are listed for localities outside the New World. For further information on published sources of distribution, check the REFERENCES section.
There are no distribution records in the database
HOSTS
Numbers in parentheses after each host family, genus, or collection method are the number of distinct collection events in the database for that host or method.
REFERENCES
The following are important recent monographs, catalogs, and supplements to catalogs that refer to this species. The specific page on which the reference is made is shown in pink at the end of the reference. In the case of Wood (1982) and Wood & Bright (1992) clicking on the reference page will link to a digital version of the work in question.
- Wood, S.L. 1982. The bark and ambrosia beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a taxonomic monograph. Great Basin Nat. Mem. 6:1-1356. [838]. (data capture complete)
- Wood, S.L., Bright,D.E. 1992. A catalog of Scolytidae and Platypodidae (Coleoptera), Part 2. Taxonomic Index. Great Basin Nat. Mem. 13:1-1553 (vol. A, B). [766]
The following are references from which host and distribution data have been input into the database. If one of the above monographs or catalogs also appears in this list, it means that most relevant collection event data have been included.
- Anonymous, 2010. Michigan State University. SCAN: Symbiota Collections of Artropods Network. http://symbiota4.acis.ufl.edu/scan/portal/collections/misc/collprofiles.php?collid=76: -.
- Atkinson, T.H.; Rabaglia,R.J.; Peck,S.J.; Foltz,J.L. 1991. New records of Scolytidae and Platypodidae from the United States and Bahamas. Coleopterists Bull. 45(2): 152-164.
- Atkinson, T.H.; Riley, E.G. 2013. Atlas and Checklist of the bark and ambrosia beetles of Texas and Oklahoma (Curculionidae: Scolytinae and Platypodinae). Insecta Mundi 292: 1-46.
- Bright, D.E. 1968. Review of the tribe Xyleborini in America north of Mexico (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Can. Entomol. 100: 1288-1323.
- Bright, D.E.; Skidmore, R.S. 1997. A Catalog of Scolytidae and Platypodidae (Coleoptera), Supplement 1 (1990-1994). A Catalog of Scolytidae and Platypodidae (Coleoptera), Supplement 1 (1990-1994): -.
- EDRR 2011. USFS Early Detection Rapid Response Database. http://www.fs.fed.us/invasivespecies/earlydetection.shtml/.
- EDRR 2014. USFS Early Detection Rapid Response Database. http://www.fs.fed.us/invasivespecies/earlydetection.shtml/.
- Rabaglia, R.J.; Valenti, M.A. 2003. Annotated list of the bark and ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) of Delaware, with new distribution records. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 105(2): 312-319.
- University of Arizona Insect Collection 2016. SCAN: Symbiota Collections of Arthropods Network. http://symbiota4.acis.ufl.edu/scan/portal/collections/misc/collprofiles.php?collid=11.
- Viloria, Z.; Villanueva, R.T.; Bessin, R.; O'Neal, P.; Ranger, C.M.; Dunwell, W. 2021. Scolytinae in Nursery and Fruit Crops of Western Kentucky and Seasonal Population Patterns of Four Invasive Ambrosia beetles. J. Entomol. Sci. 56 (3): 374-386.
- Weber, B.C., MacPherson, J.E. 1991. Seasonal Flight Patterns Of Scolytidae (Coleoptera) In Black-Walnut Plantations In North-Carolina And Illinois. Coleopterists Bull. 45(1): 45-56.
- Wood, S.L. 1982. The bark and ambrosia beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a taxonomic monograph. Great Basin Nat. Mem. 6: 1-1356.
- Wood, S.L. 2007. Bark and ambrosia beetles of South America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Monte L. Bean Science Museum. Provo, Utah: 1-900.
 Distribution Map
Distribution Map

Maps automatically open at the center of the plotted points and the scale is set to encompass all map points. Maps can be resized (scale bar at upper left) and the center moved (place cursor over map and drag) to see other parts of the distribution of the species. Clicking on a map marker will pull up collection event data and a literature citation if present. If any errors are found, please refer to the "series code" which is a unique identifier for a database record in any communications). Coordinates have not been entered for all collection records. Localities outside the New World are not plotted, even though they are listed in the distribution summary and in the table of records.
There are no distribution records in the database
 Collection Records
Collection Records
There are no distribution records in the database
Return to top of page
